
You can kill the container with the docker kill command: $docker kill a189a4db0f7 Check all the running containers: $ docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED a189a4db0f7 apache "/usr/sbin/apache2ctl" 10 seconds ago It will take some time, then you should see successful build like this: Successfully built e7083fd898c7 Successfully tagged ng:latest Swapnil:apache swapnil$ Then, build the image: docker build -t apache.
#Osx docker image install
Next, create a directory for Apache inside the dockerproject: $ mkdir apacheĬreate a Dockerfile inside Apache folder: $ nano DockerfileĪnd paste these lines: FROM ubuntu MAINTAINER Kimbro Staken version: 0.1 RUN apt-get update & apt-get install -y apache2 & apt-get clean & rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/* ENV APACHE_RUN_USER www-data ENV APACHE_RUN_GROUP www-data ENV APACHE_LOG_DIR /var/log/apache2 EXPOSE 80 CMD
#Osx docker image password
To log into DockerHub from the command line, just run: $ docker loginĮnter your username and password and you are logged in. You may also want to create an account on DockerHub and log into your account before building images, in case you are pulling something from DockerHub. Building a whole LAMP stack can be challenging, so we are going create a simple Apache server image with Dockerfile.ĭockerfile is basically a set of instructions to install all the needed packages, configure, and copy files. You can see all three images: dockp, Ubuntu, and hello-world, which I created a few weeks ago when working on the previous articles of this series. Let’s check all the Docker images you have in your directory: $docker images REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE dockp latest 2a4cca5ac898 1 hour ago 111MB ubuntu latest 2a4cca5ac898 1 hour ago 111MB hello-world latest f2a91732366c 8 weeks ago 1.85kB You can run all native Ubuntu commands and CLI utilities. You should see root prompt: means you are literally running bare minimal Ubuntu inside Linux, Windows, or macOS. It’s time to run and test your image: $ docker run -it Ubuntu

(Note the dot at the end of the command.) This should build successfully, so you’ll see: Sending build context to Docker daemon 2.048kB Step 1/1 : FROM ubuntu -> 2a4cca5ac898 Successfully built 2a4cca5ac898 Successfully tagged dockp:latest
Now create your new image and provide it with a name (run these commands within the same directory): $ docker build -t dockp. Now create a Dockerfile inside the dockerprojects directory using your favorite text editor I prefer nano, which is also easy for new users. In this example, I will use Ubuntu.īefore we start building our images, let’s “containerize” them! By this I just mean creating directories for all of your Docker images so that you can maintain different projects and stages isolated from each other. You can get Alpine (the official distro used by Docker Editions), Ubuntu, BusyBox, or scratch. We are going to use prebuilt images to get the base Linux subsystem, as it’s a lot of work to build one from scratch. There are prebuilt images available on DockerHub that you can use for your own project, and you can publish your own image there. In this article, we will get a basic understanding of creating Docker images.
#Osx docker image how to
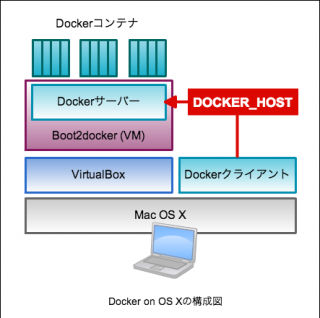
In the previous article, we learned about how to get started with Docker on Linux, macOS, and Windows.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
